Introduction to RAG¶
- RAG(Retrieval-Augmented Generation) combines retrieval and generation to enhance AI model responses
- Retrieves relevant knowledge from external data sources and feeds it into the model
-
Provides more accurate, grounded, up-to-date answers than standalone LLMs
-
Core use cases:
- enterprise knowledge assistants
- chatbots with factual grounding
- document Q&A
-
RAG workflow:
- Query → Vector DB finds closest vectors
- Matched text fed into LLM
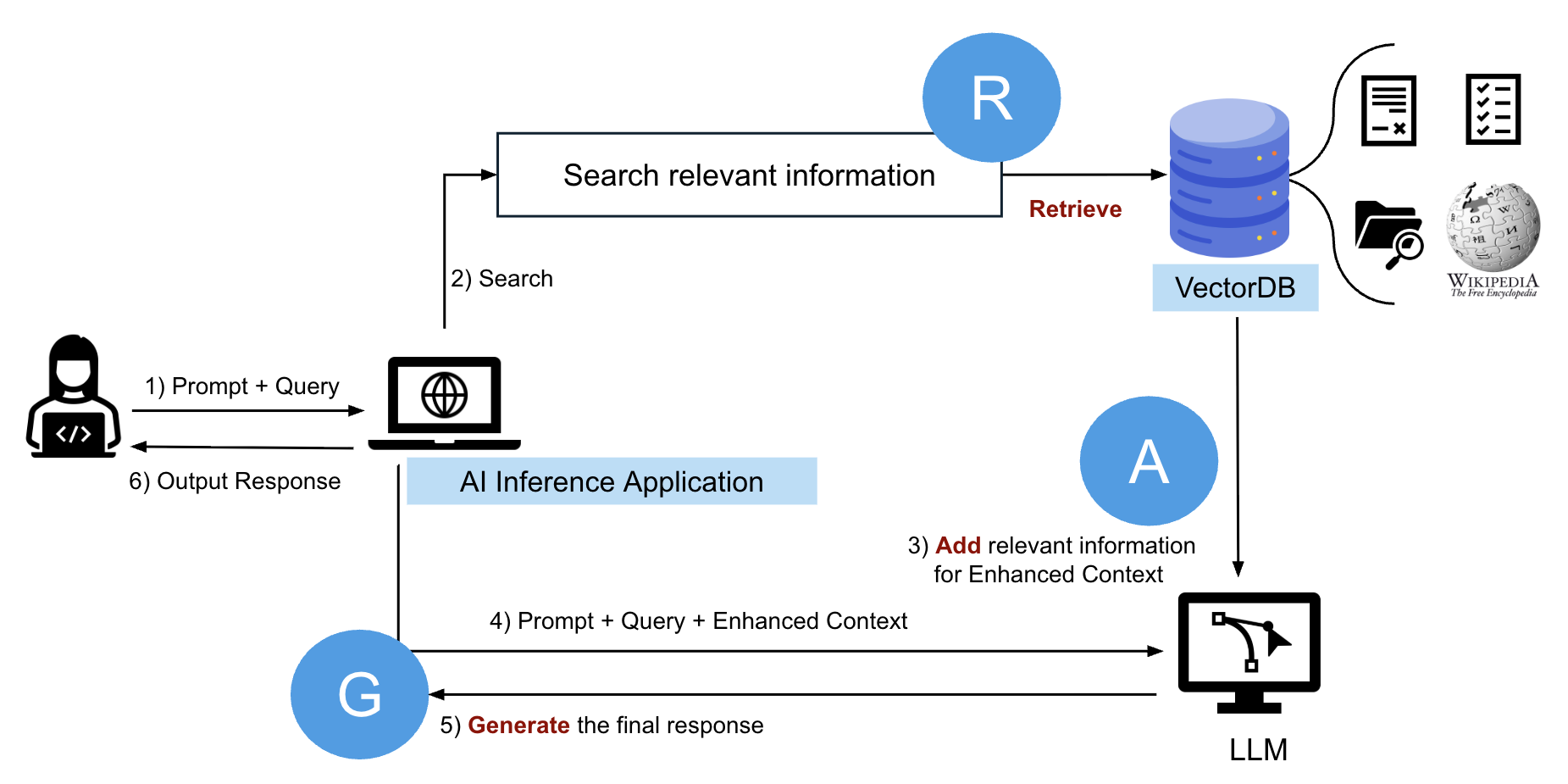 RAG and VectorDB
RAG and VectorDB
Introduction to Vector Databases¶
- Vector databases store and search high-dimensional vectors generated by AI models
- Their goal is to provide fast, accurate, scalable similarity search
- Core use cases:
- RAG
- semantic search
- recommendation systems
- anomaly detection
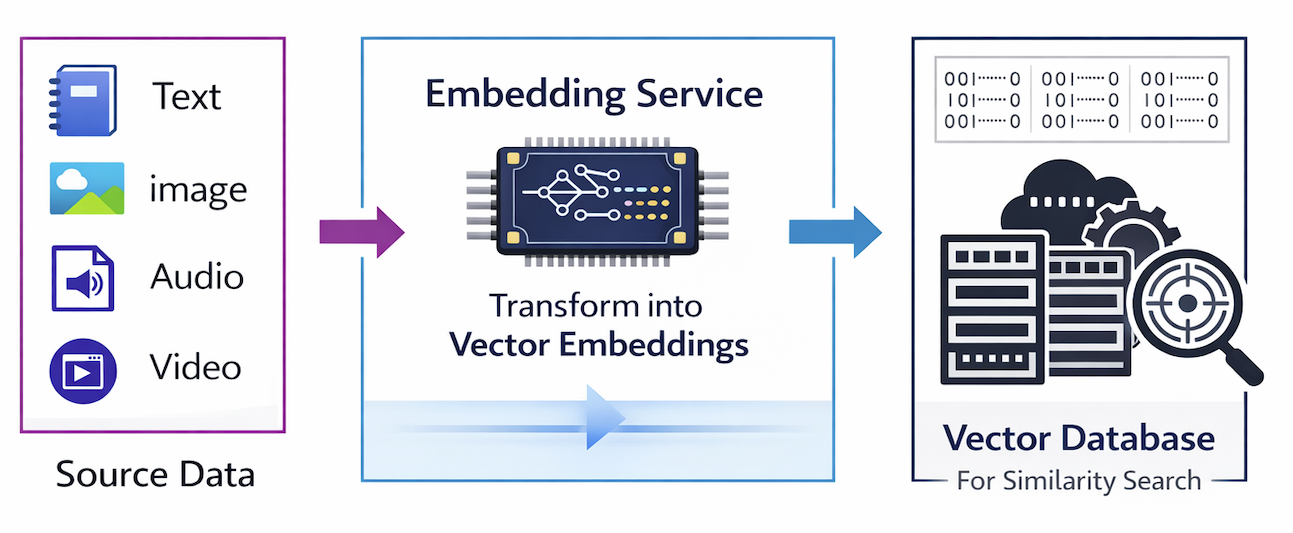
What Are Vectors?¶
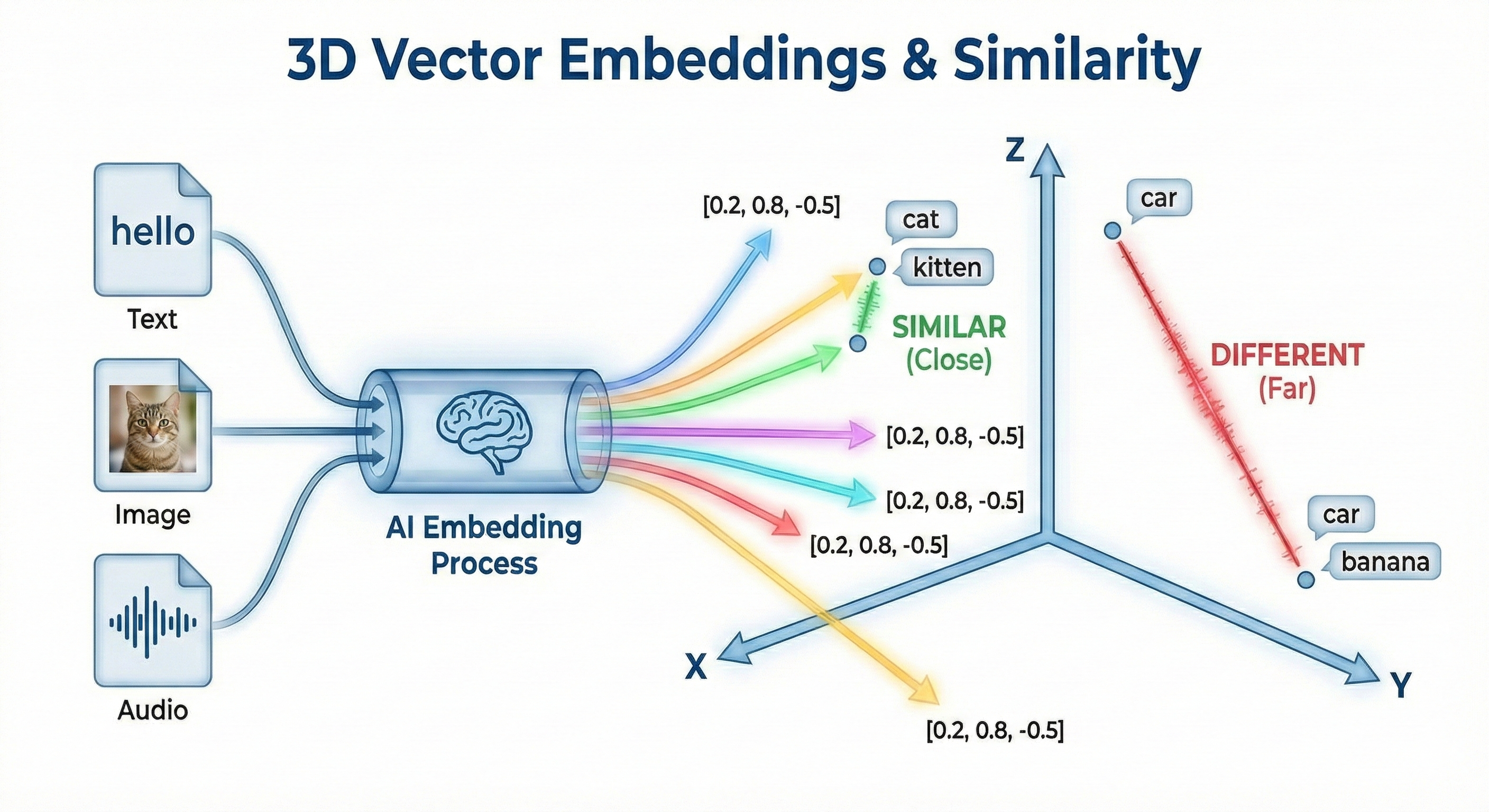
- A vector is a list of numbers representing meaning or features
- AI models convert text, images, audio, or video into embeddings
- Similar items → vectors close in space
- Example similarities/differences:
- “cat” ↔ “kitten” (similar)
- “car” ↔ “banana” (different)
 ¶
¶
Why Vector Databases?¶
- Traditional databases cannot efficiently search high-dimensional vectors
- Vector DBs support Approximate Nearest Neighbor (ANN) search
- ANN enables millisecond-level retrieval at billion scale
- Benefits:
- Fast search
- High scalability
- Built-in indexing structures
- Real-time updates
Key Operations¶
- Store vectors
- Index vectors
- Search using similarity metrics (cosine, dot product, Euclidean)

- The output will produce a value ranging from -1 to 1, indicating similarity where -1 is non-similar, 0 is orthogonal (perpendicular), and 1 represents total similarity.

- Filter using metadata (tags, categories, user IDs)
Popular Vector Databases¶
- Milvus – open-source, cloud-native
- Pinecone – fully managed
- Weaviate – plugin-based, modular
- Qdrant – Rust-based, lightweight
- FAISS – library for vector search (not a full DB)
When to Use a Vector Database¶
- You need semantic search
- You handle multimodal data
- You expect large-scale datasets
- You need low-latency retrieval