AI Training & AI Inference Explained
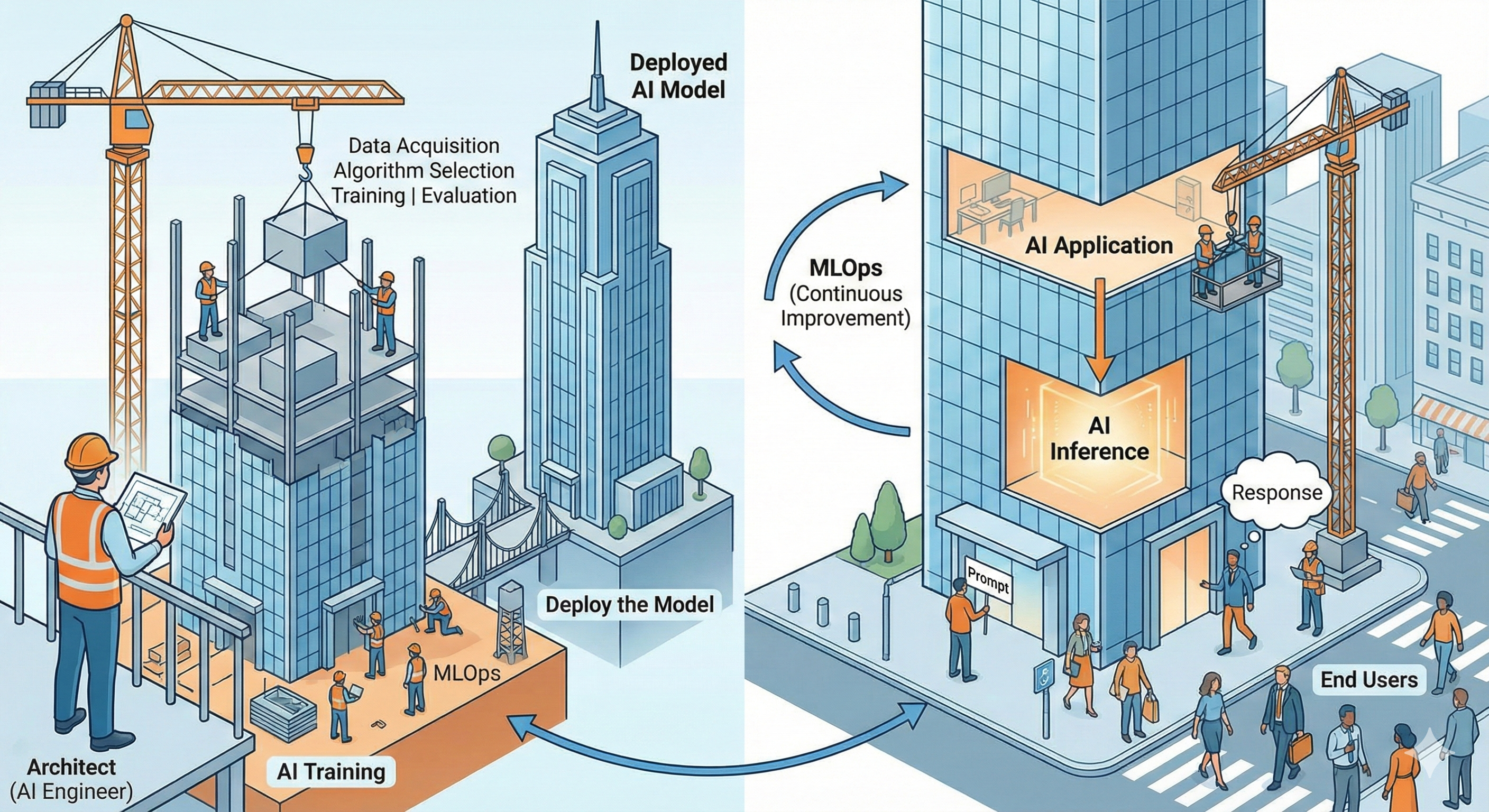
- AI Training builds and refines the model’s intelligence through data collection, algorithm selection, optimization, and evaluation.
- Deployment makes the trained model available for real-world use within an AI application.
- AI Inference applies the model’s learned knowledge to user inputs(prompts) and generates meaningful outputs in real time.
- AI applications connect end users to the model, delivering responses powered by the inference process.
- GPUs accelerate both training(data processing, optimization, evaluation) and inference(fast, real-time predictions)
End-to-End AI Training Architecture
- AI training is a step-by-step process that transforms raw data into a usable model
- Overall flow: collect → prepare → train → evaluate → package & store
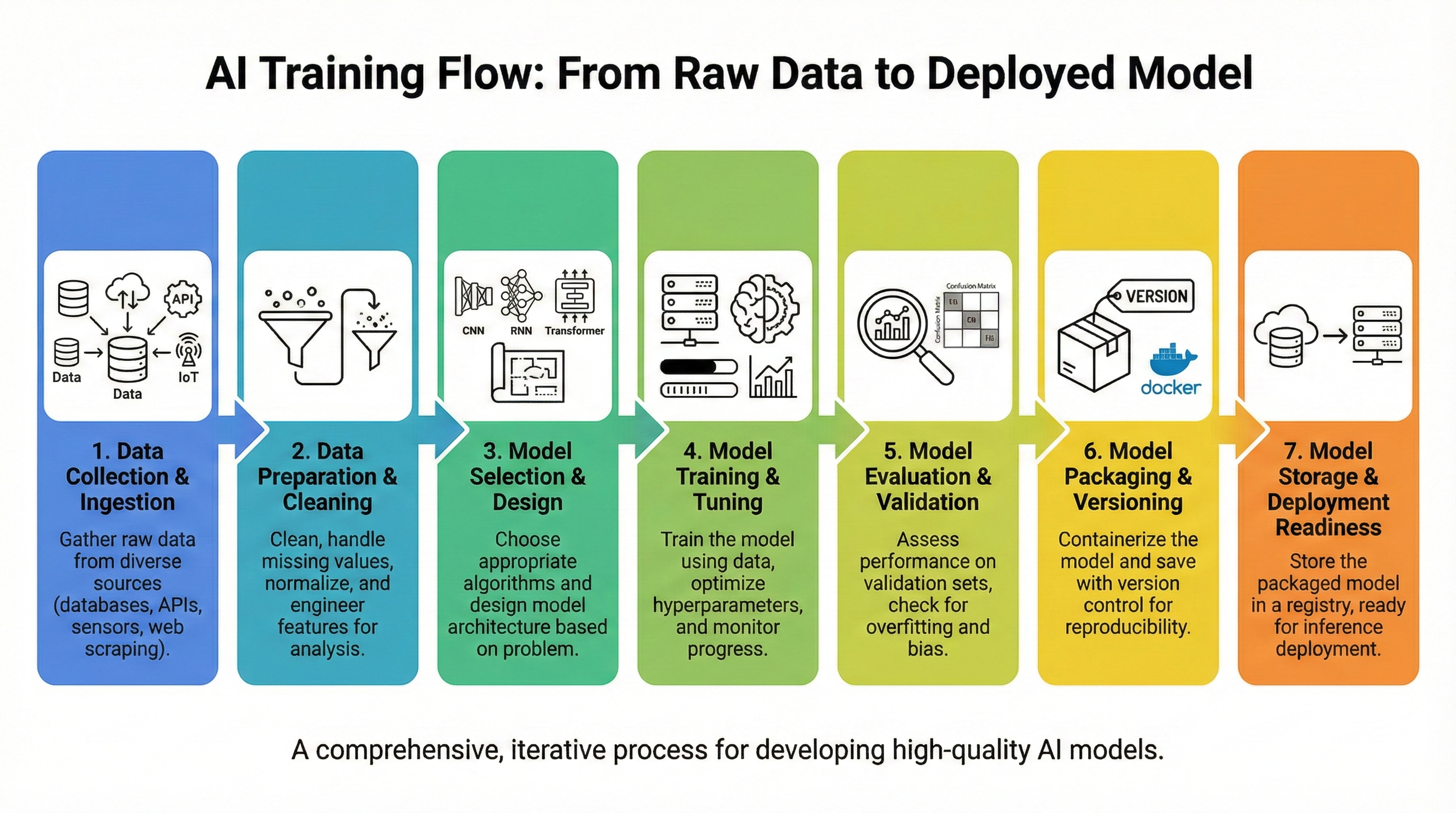
Training Flow Overview
- Data is collected from storage, logs, or databases
- The data is cleaned and prepared for training
- GPU servers train the model using the processed data
- The model is evaluated for accuracy and quality
- The final model is packaged and saved in a registry
Data Ingestion and Preparation
- Data sources include object storage, databases, log files, and CSVs
- Data cleaning fixes missing values, errors, and inconsistent formats
- Text is tokenized, images are resized, numeric values are normalized
- Labels are added for supervised learning tasks
- Common tools: Pandas, Spark, Airflow, HuggingFace Datasets
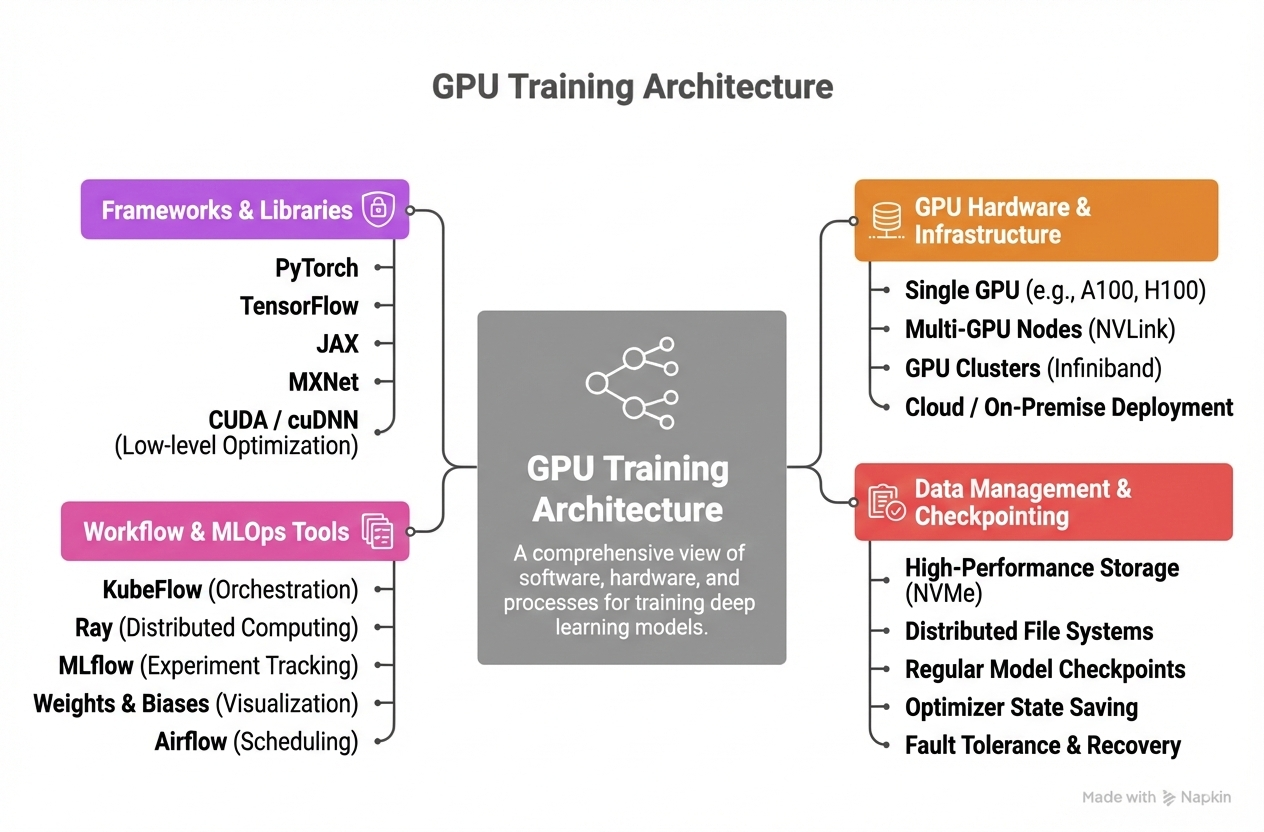
GPU Training Architecture
- Training uses GPU servers because they handle large matrix operations efficiently
- Training can run on a single GPU or scale across multiple GPUs
- Checkpoints are saved so progress isn’t lost
- Jobs can be automated through workflow tools
- Typical frameworks:
- PyTorch
- TensorFlow
- Kubeflow
- Ray
Model Evaluation
- The model is tested with unseen data
- Key checks include:
- accuracy
- error rate
- speed
- reliability
- For LLMs, evaluation also checks safety, consistency, and hallucination
- Evaluation results help determine whether the model is ready or needs improvement
Model Packaging and Registry
- The trained model is exported into an inference-ready format
- Supporting files (tokenizers, configs) are saved together
- The model is stored in a registry for version tracking
- Example: MLflow, HuggingFace Hub, S3 folders
- Versioning allows easy deployment, rollback, and collaboration
×




