End-to-End AI Inference Architecture¶
- AI inference is the process of running a trained model to generate predictions
- Uses pre-trained weights to produce outputs from new inputs
- The goal: deliver fast, reliable, and scalable responses
- User-facing applications depend heavily on predictable low latency
- Overall flow: load model → serve model → route requests → scale automatically → monitor performance
- Represents the full lifecycle from model loading to production monitoring
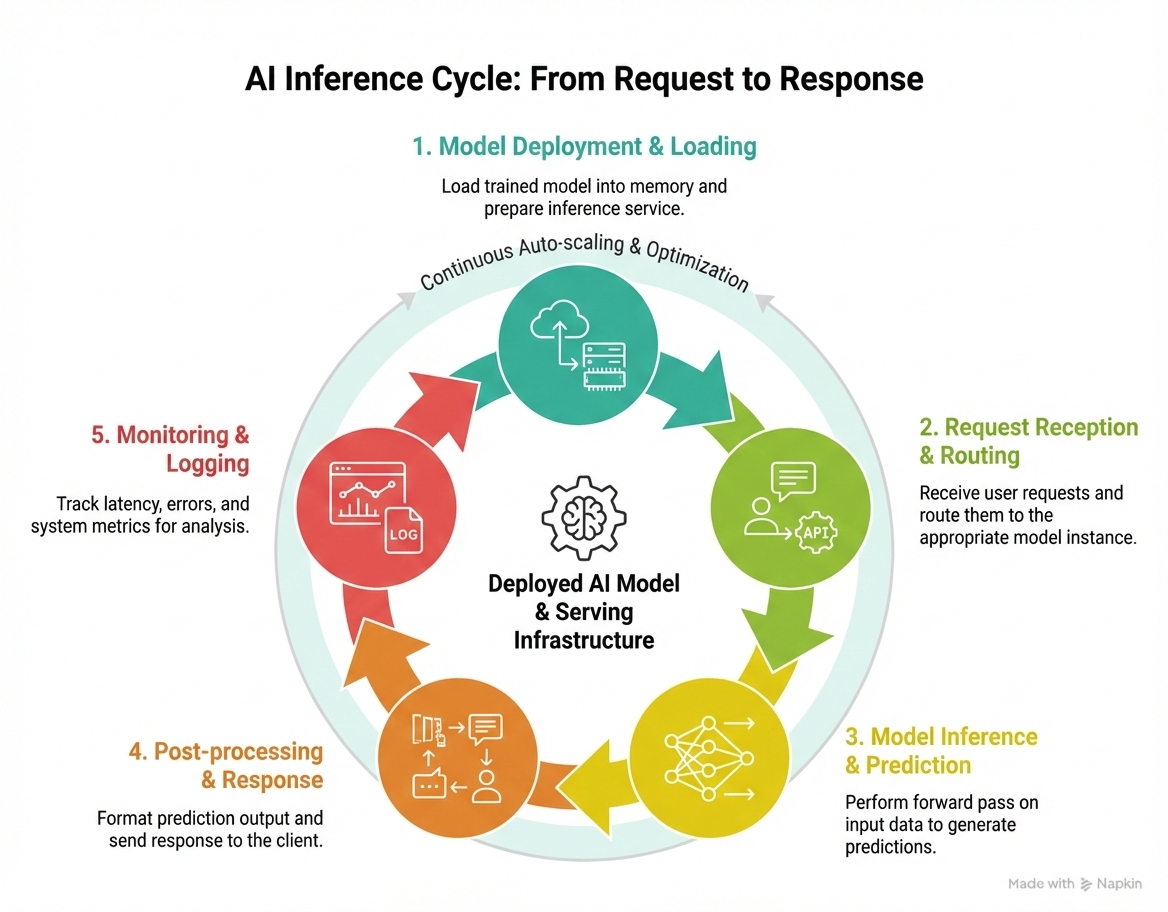
Model Loading and Serving¶
- Models are loaded into GPU/CPU memory using an inference server
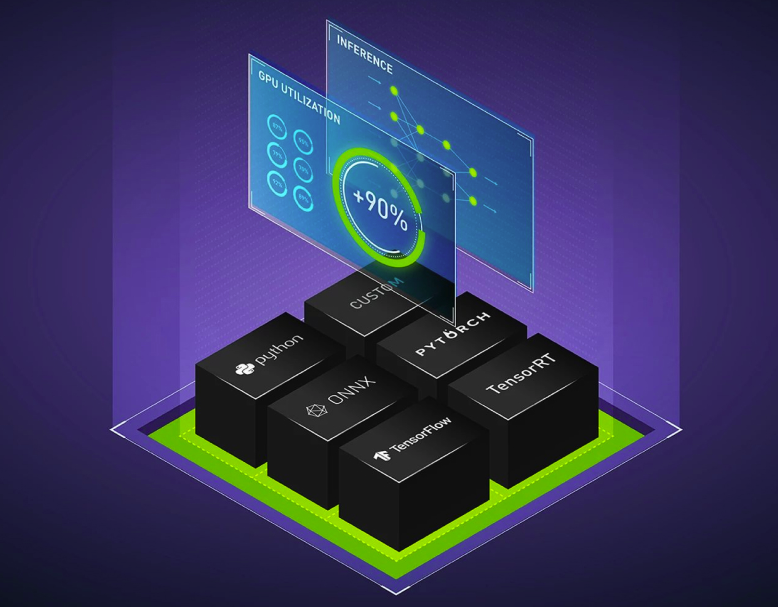
- Popular serving systems include:
- NVIDIA Triton Inference Server : Multi-framework support with optimized scheduling
- TorchServe : Good for PyTorch-based services
- TensorFlow Serving : Highly optimized for TensorFlow models
- Ollama, vLLM : optimized for LLMs, Excellent continuous batching and high throughput
- Models can be optimized to reduce inference latency
- ONNX, TensorRT, quantization, pruning, and graph optimizations
- Reduces compute cost while maintaining accuracy
Inference Server, Ref.: https://developer.nvidia.com/dynamo-triton
Performance and Monitoring¶
- Key inference metrics include:
- latency – average & p99 latency for user experience
- Lower latency → better UX, especially for LLMs & real-time apps
- throughput – requests/second or tokens/second
- Higher throughput → better hardware utilization
- GPU utilization – measures processing efficiency
- Prevents underuse or overload
- memory usage – especially VRAM usage
- Larger models require precise memory planning
- Logs and metrics are collected using tools like:
- Prometheus, Grafana, ELK
- Provides dashboards to visualize real-time performance
- Monitoring ensures reliable, stable inference service
- Detects regression, degradation, or scaling issues early