Learning Paradigms Explained¶
AI systems can learn in different ways depending on how much supervision the data provides.
Each paradigm offers different strengths, trade-offs, and typical use cases.
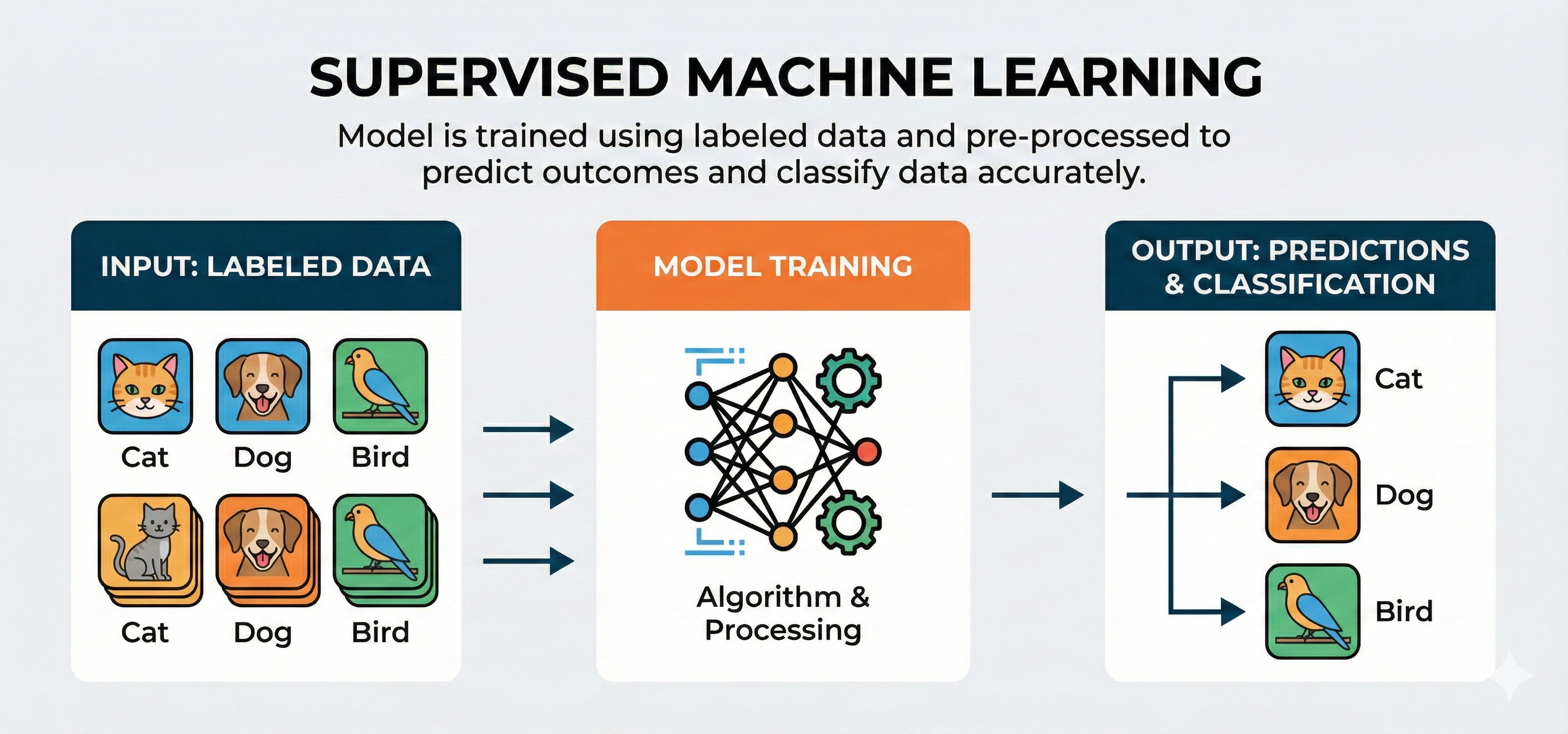
Supervised Learning¶
- Trains on labeled data where both input (x) and target output (y) are known.
- Highest accuracy when high-quality labels exist
- Most widely used paradigm in real-world ML systems
- Image classification (cat vs dog) / Regression (house price prediction)
- Speech recognition / Fraud detection
 ¶
¶
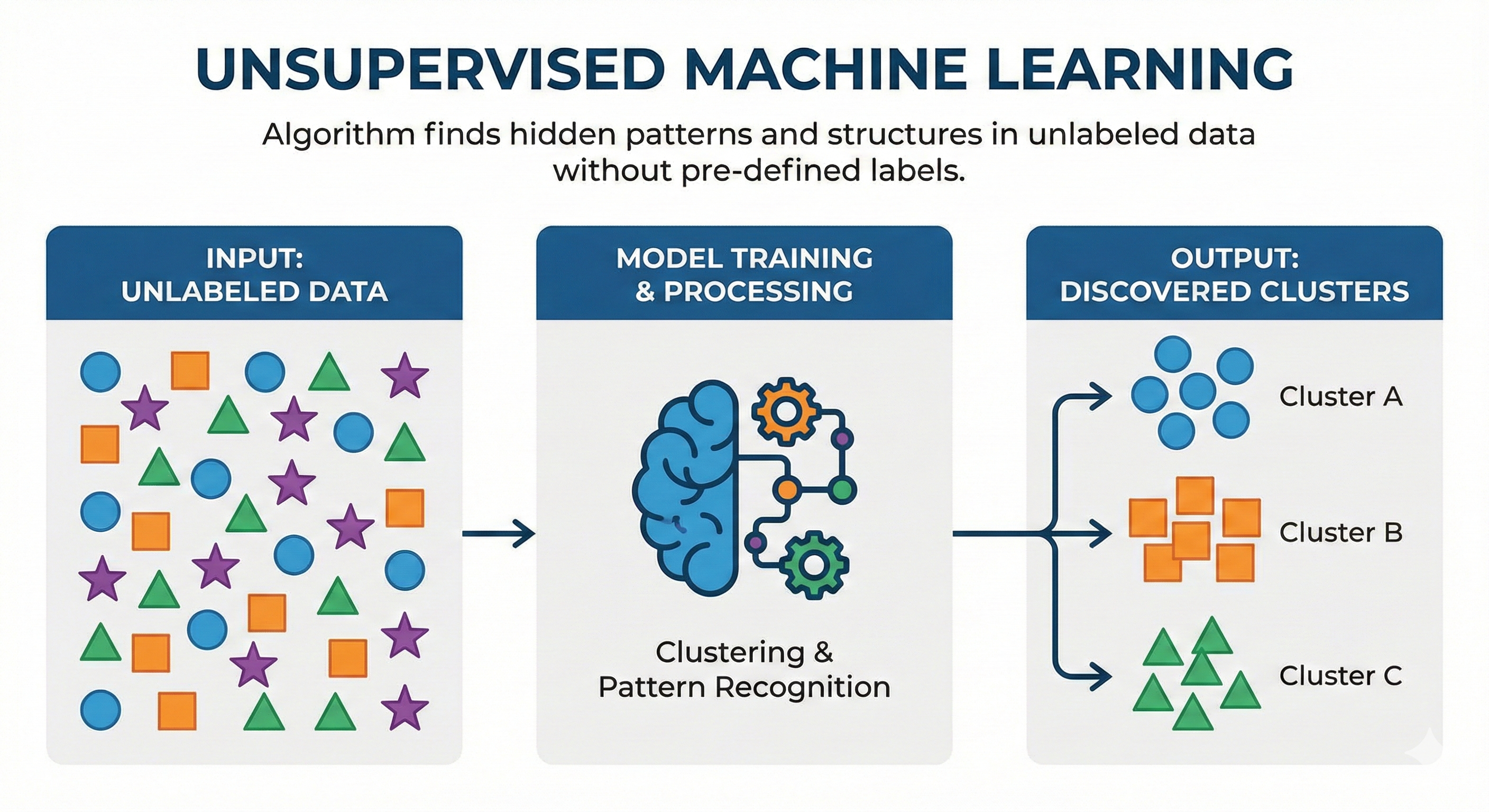
Unsupervised Learning¶
Learns from unlabeled data by discovering hidden patterns or structure.
- No predefined targets
- Finds meaningful clusters, groups, or latent representations
- Useful when labels are unavailable or too costly
- Clustering users or behaviors (e.g., K-means)
- Customer segmentation / Embedding generation for retrieval
 ¶
¶
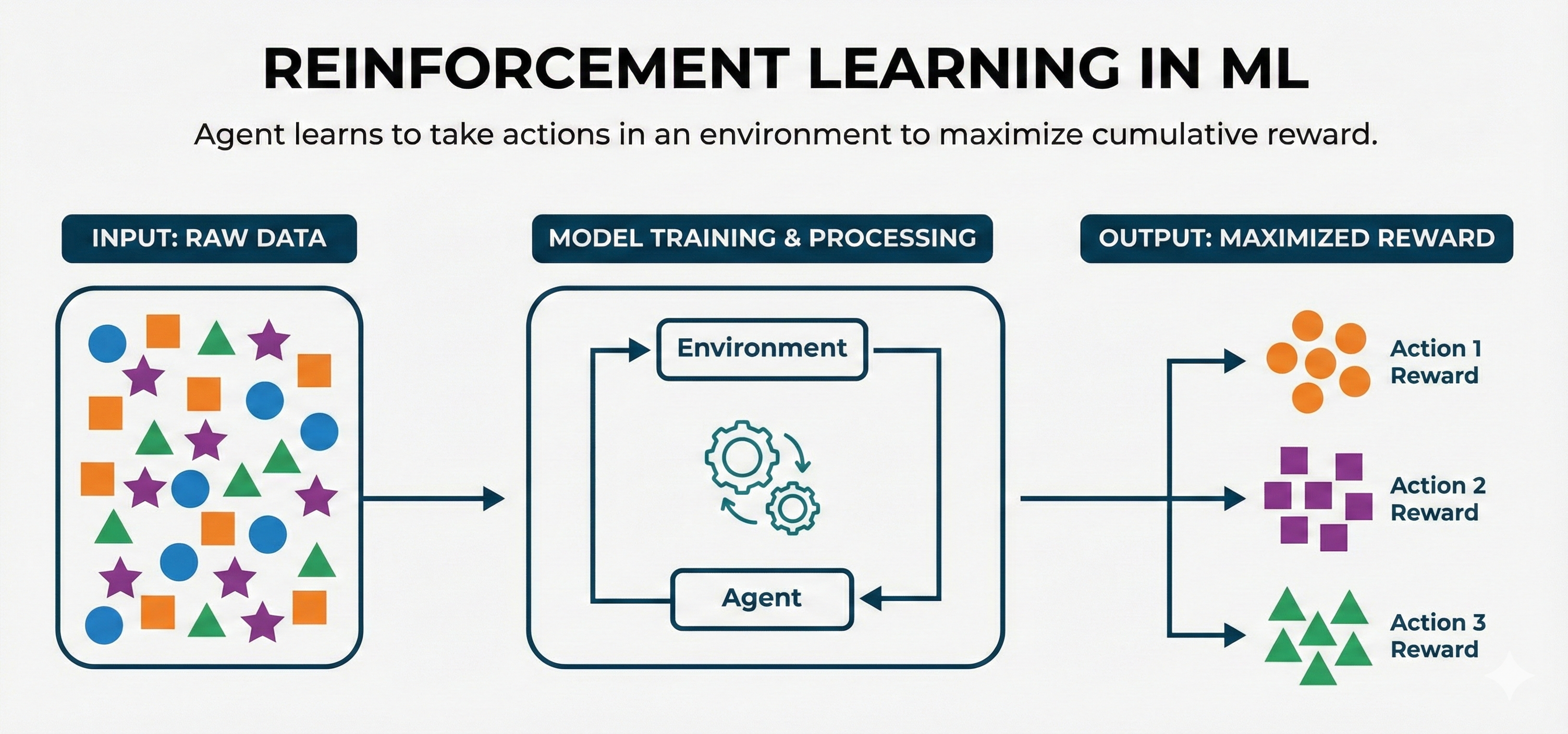
Reinforcement Learning¶
- An agent learns by taking actions in an environment and receiving rewards or penalties.
- Learning through trial and error
- Policy improves over time based on reward signals
- Suited for sequential decision-making
- Game-playing (Atari, Go, StarCraft) / Robotics and autonomous navigation
- Industrial control systems / Recommendation systems (bandit optimization)