Foundations of Modern AI¶
- Modern AI is driven by deep learning and large-scale neural networks
- Progression: early neural nets → specialized architectures → Transformers powering today's LLMs
- Core principle: learn hierarchical patterns from raw data (images, text, audio, logs, etc.)
AI Hierarchy¶
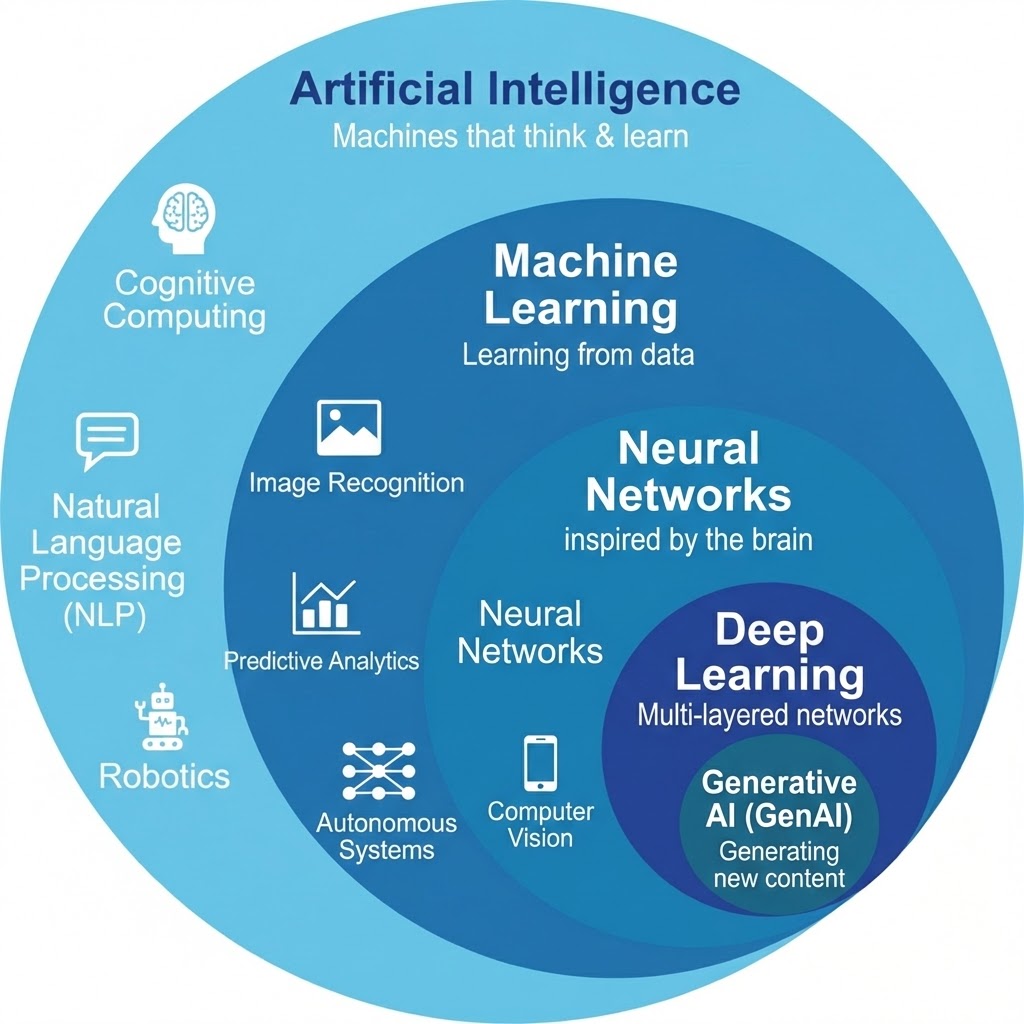
- Artificial Intelligence is the broad field of making machines solve problems like humans
- Machine Learning is a subset of AI that learns patterns from data
- Neural Networks mimic the structure of the brain to recognize complex patterns
- Deep Learning is a deeper, layered form of neural networks used in vision and language tasks
Evolution of Neural Network Architectures¶
- A Neural Network is a machine-learning model inspired by how the human brain processes information, used to learn patterns from data and make predictions or decisions.
- This is a conceptual comparison of major neural network architectures, showing what kinds of problems each model is mainly used for.
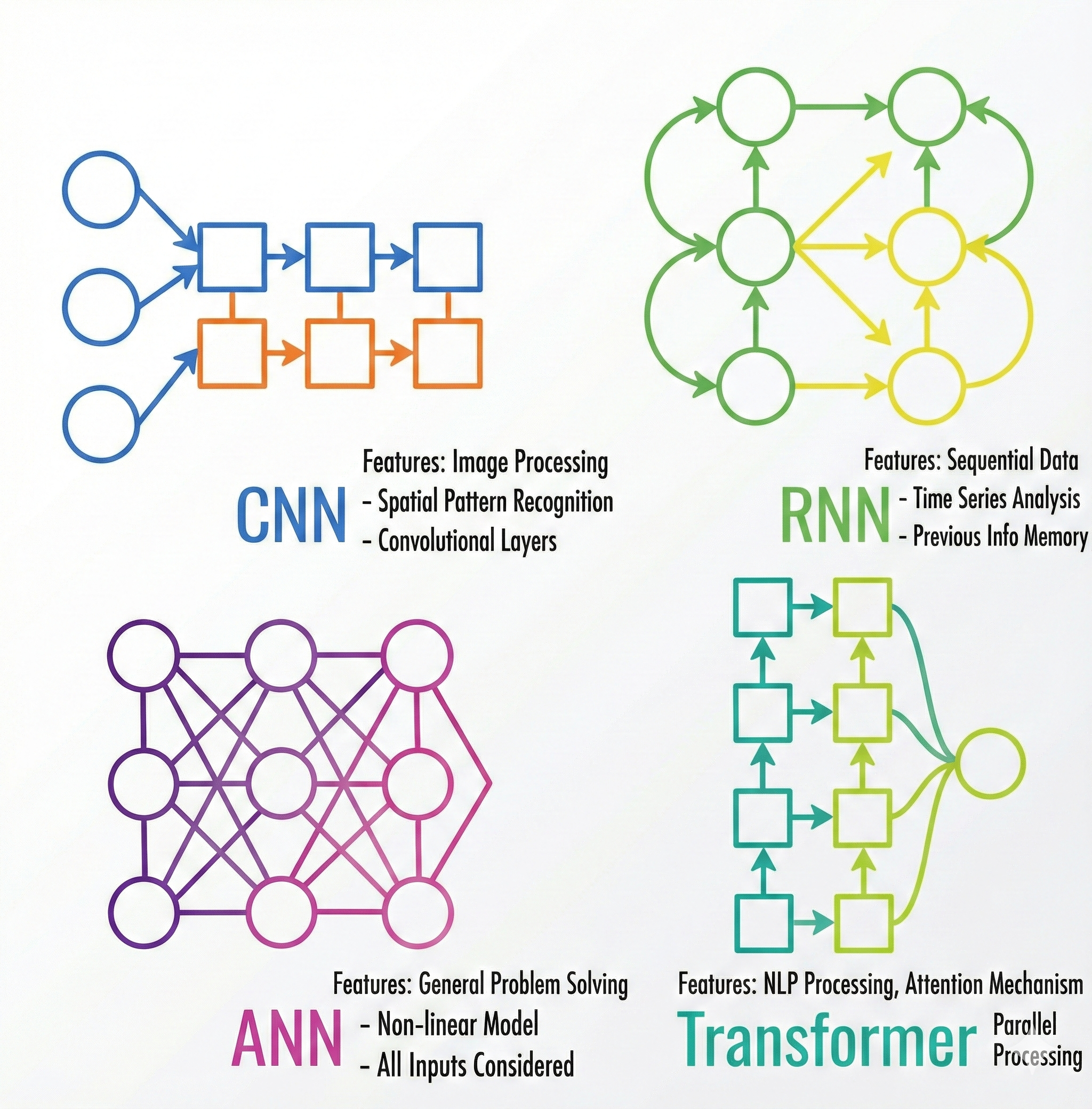
Neural Networks (NN)¶
- Basic fully connected layers
- Learn simple to moderately complex patterns
- Strengths: easy to train, general-purpose
- Limitations: cannot capture spatial or sequential structure
- Use cases: classification, regression, tabular data
Convolutional Neural Networks (CNN)¶
- Convolution filters detect local spatial features
- Hierarchical representation: edges → shapes → objects
- High performance in computer vision tasks
- Use cases: image classification, detection, segmentation, medical imaging
Recurrent Neural Networks (RNN / LSTM / GRU)¶
- Designed for sequential/time-series data
- Capture order, temporal context, and dependencies
- LSTM/GRU introduce gating to reduce vanishing gradients
- Use cases: speech recognition, time-series forecasting, early NLP systems
Transformer¶
- Replaces recurrence with attention mechanism
- Enables parallel sequence processing (GPU-efficient)
- Learns long-range relationships with high accuracy
- Foundation of modern LLMs (GPT, Llama, Mistral, etc.)
- Use cases: LLMs, translation, RAG pipelines, multimodal AI
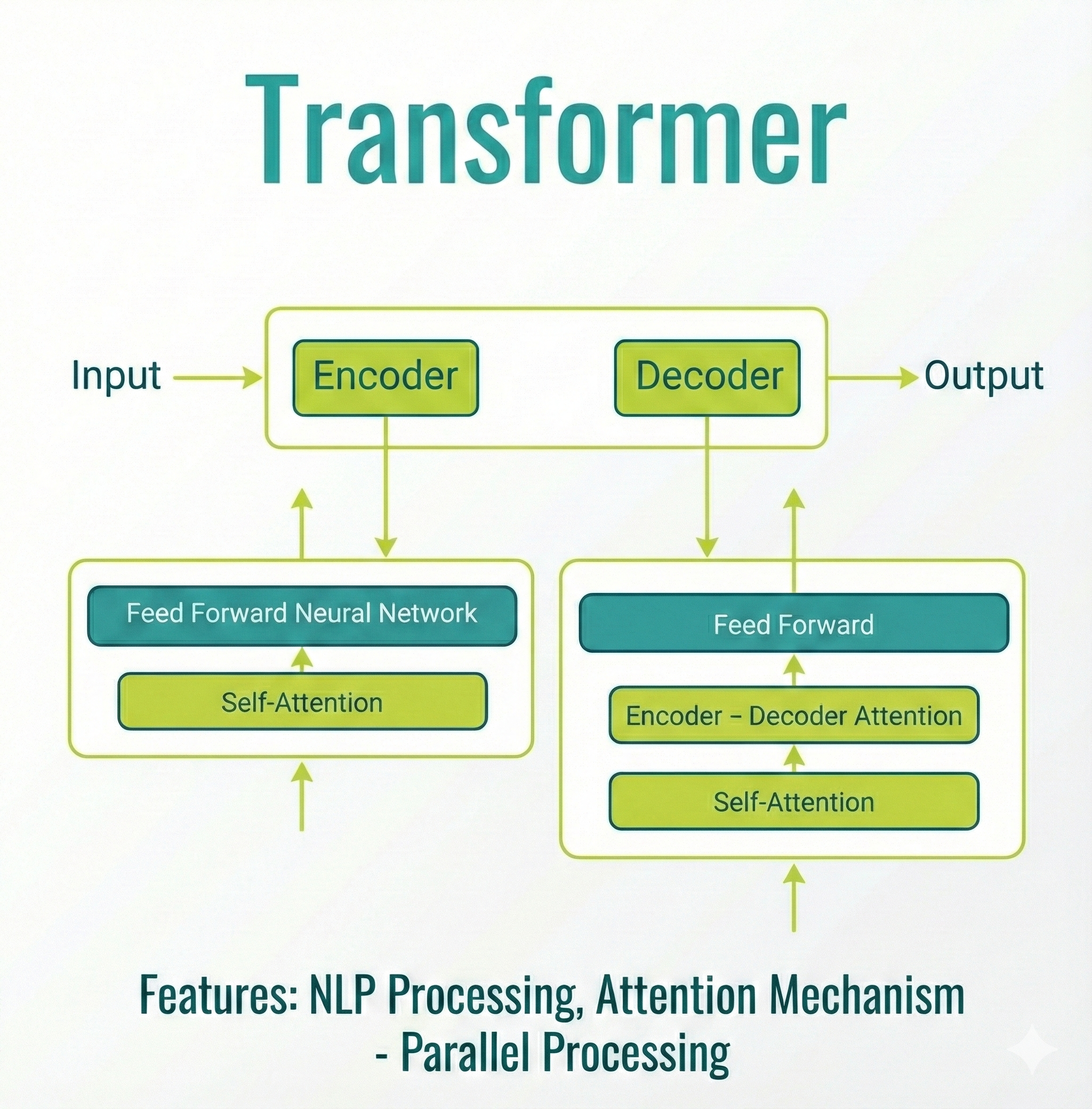
Why Transformers Won¶
- Attention mechanism identifies important parts of the input dynamically
- Parallel computation → massive acceleration on GPUs
- Scales extremely well with model/data size
- Works across modalities: text, image, audio, code
- Supports modern ecosystems: RAG, fine-tuning, agents, multimodal processing
Architecture Summary Table¶
| Model | Key Idea | Strengths | Typical Use Cases |
|---|---|---|---|
| Neural Network | Fully connected layers | Simple, general-purpose | Classification, regression |
| CNN | Convolution filters | Vision accuracy; spatial hierarchy | Image tasks, detection, segmentation |
| RNN / LSTM | Recurrent & gated memory | Sequence modeling | Speech, time-series, sequential NLP |
| Transformer | Attention mechanism | Parallelism, scalability, long-context | LLMs, translation, RAG, multimodal |
---